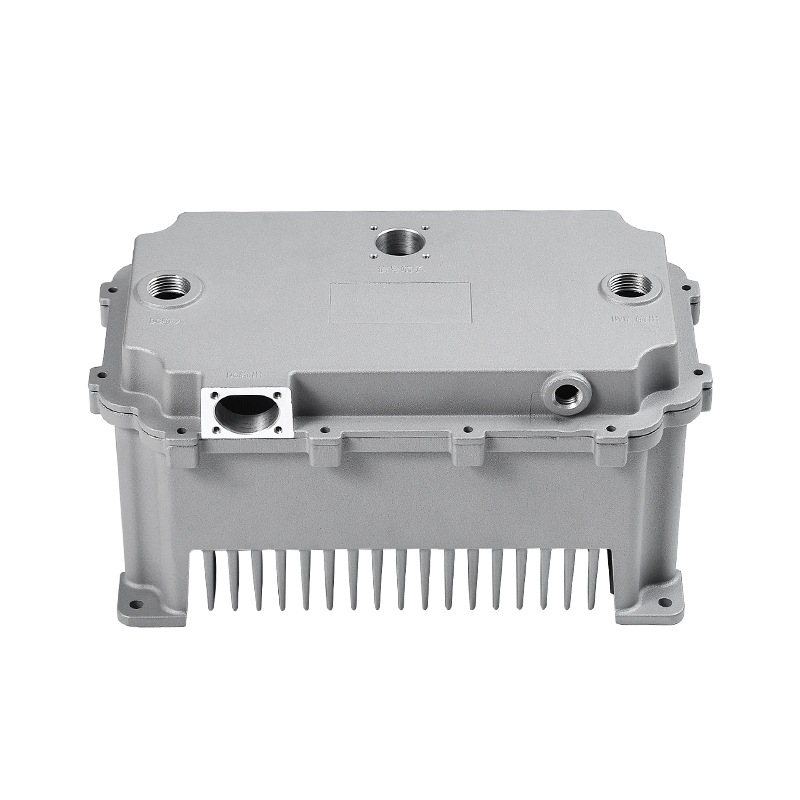
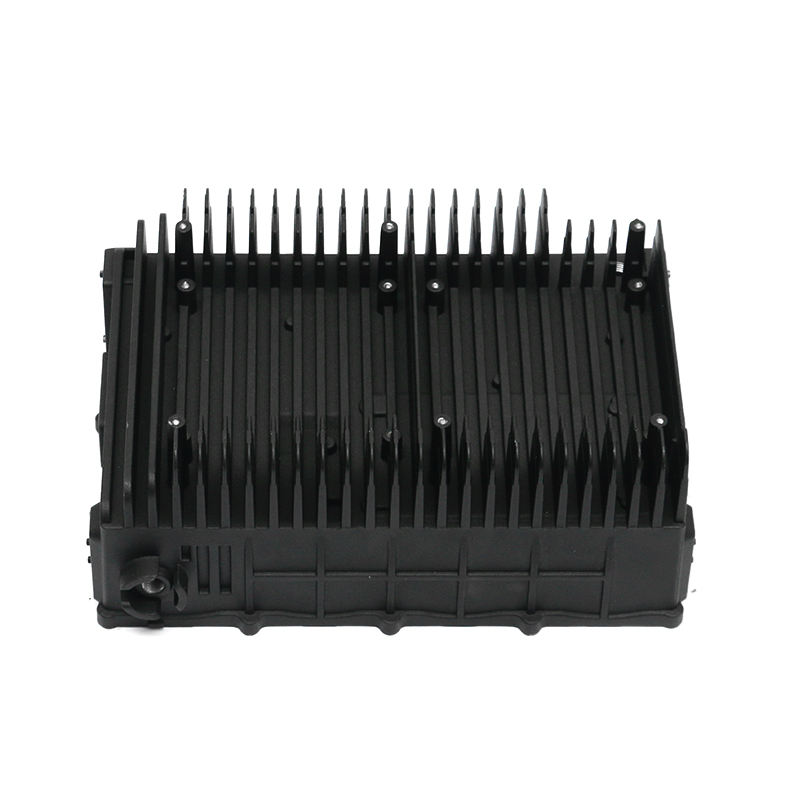
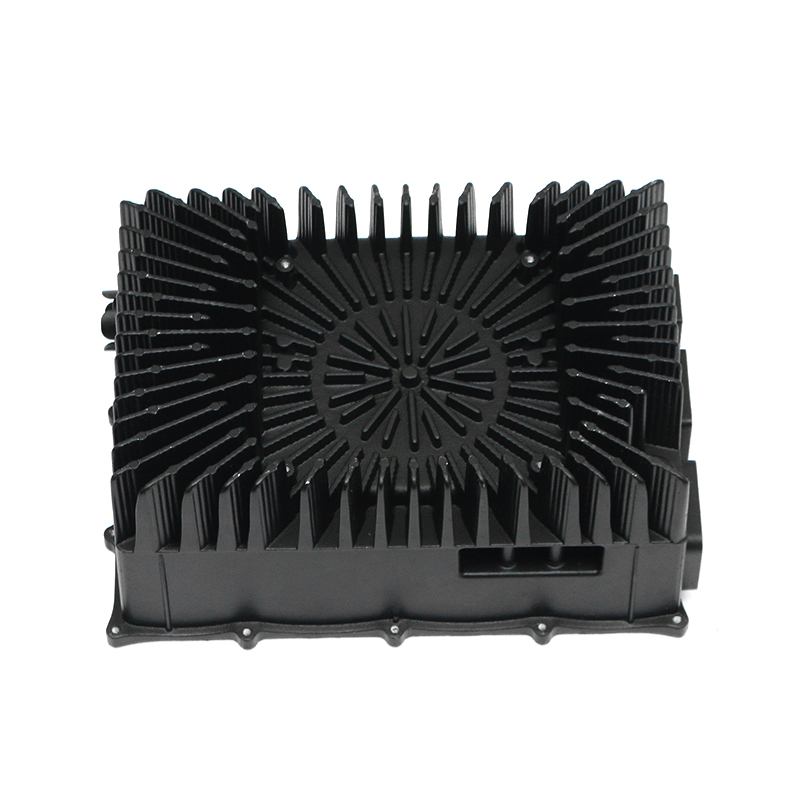
el bomba de agua del coche Desempeña un papel fundamental en el mantenimiento de una circulación eficiente del refrigerante en todo el motor al hacer circular continuamente refrigerante (generalmente una mezcla de agua y anticongelante) a través del bloque del motor, el radiador y el sistema de enfriamiento. Esto ayuda a mantener el motor a una temperatura de funcionamiento óptima transfiriendo calor lejos del motor y evitando que se sobrecaliente.
el car water pump is typically driven by the engine's crankshaft via a belt, chain, or sometimes by an electric motor (in the case of electric water pumps). As the pump rotates, it uses an impeller to move coolant through the engine.The impeller consists of several blades or vanes that direct the coolant towards the engine block and radiator. As the impeller spins, it creates a pressure differential that draws coolant into the pump and forces it into the engine's cooling passages.
el car water pump sucks coolant from the bottom of the radiator (or coolant reservoir) through a suction inlet. The coolant is then passed through the pump's impeller, which increases the coolant's velocity and pressure as it is pushed out.
el coolant is directed to flow through the engine block and cylinder head, where it absorbs the heat generated by the combustion process. It then returns to the radiator, where the heat is released into the surrounding air, and the coolant is cooled before being recirculated by the water pump.
el thermostat plays a crucial role in regulating the temperature of the coolant and ensuring that it circulates at the optimal temperature range for engine efficiency. When the engine is cold, the thermostat remains closed to prevent coolant flow to the radiator, allowing the engine to warm up faster.
Cuando el motor alcanza su temperatura de funcionamiento, el termostato se abre, permitiendo que el refrigerante fluya libremente hacia el radiador. Esto garantiza que la bomba de agua haga circular refrigerante solo cuando el motor alcance la temperatura correcta para un enfriamiento eficiente.
el car water pump ensures the coolant is circulated at the correct pressure and flow rate to achieve efficient heat dissipation. If the flow rate is too low, the coolant won't absorb enough heat from the engine, which can lead to overheating. Conversely, if the flow rate is too high, it could result in unnecessary energy consumption and reduced overall system efficiency.
el pump is designed to match the engine's cooling demands by adjusting the flow based on factors such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and load conditions. Some modern vehicles use electronic control systems to regulate the speed of electric water pumps, adapting the flow to real-time conditions.
el car water pump must be able to maintain an effective coolant circulation rate under varying engine conditions. As engine speed increases (e.g., during acceleration), the water pump speeds up to increase coolant flow, ensuring that the engine remains adequately cooled under high-performance conditions.
Por otro lado, cuando el motor está en ralentí o funcionando a bajas velocidades, la bomba puede reducir la velocidad, reduciendo el flujo de refrigerante para conservar energía.
La mayoría de los sistemas de refrigeración tienen un circuito de derivación que permite que parte del refrigerante fluya directamente desde la bomba de agua del automóvil al motor sin pasar por el radiador. Esto ayuda a que el motor alcance la temperatura de funcionamiento más rápido, especialmente durante los arranques en frío, al garantizar que el refrigerante circule y se caliente incluso cuando el termostato está cerrado.
Una vez que se abre el termostato, el refrigerante fluye a través del radiador, donde se enfría antes de regresar al motor. Esto ayuda a evitar que el motor se sobrecaliente al ralentí o al conducir a baja velocidad.
En los vehículos modernos, especialmente los híbridos y eléctricos, algunas bombas de agua para automóviles están diseñadas para variar el flujo de refrigerante en función de las necesidades en tiempo real del motor y del sistema de refrigeración. Por ejemplo, una bomba de agua eléctrica puede ser regulada por la ECU (Unidad de control electrónico) del vehículo para ajustar el caudal según la temperatura, la carga del motor y la velocidad.
Productos recomendados
Los usuarios confían profundamente en los productos proporcionados por empresas famosas.